Table of Contents
In the heart of Southeast Asia, Brunei Darussalam’s economic and social development heavily relies on a robust and stable electrical power system. As the nation continues to grow and diversify its economy, the importance of power system stability in electrical engineering cannot be overstated. This article explores the critical role of power system stability in Brunei’s infrastructure and the challenges and solutions in maintaining it.
Understanding Power System Stability
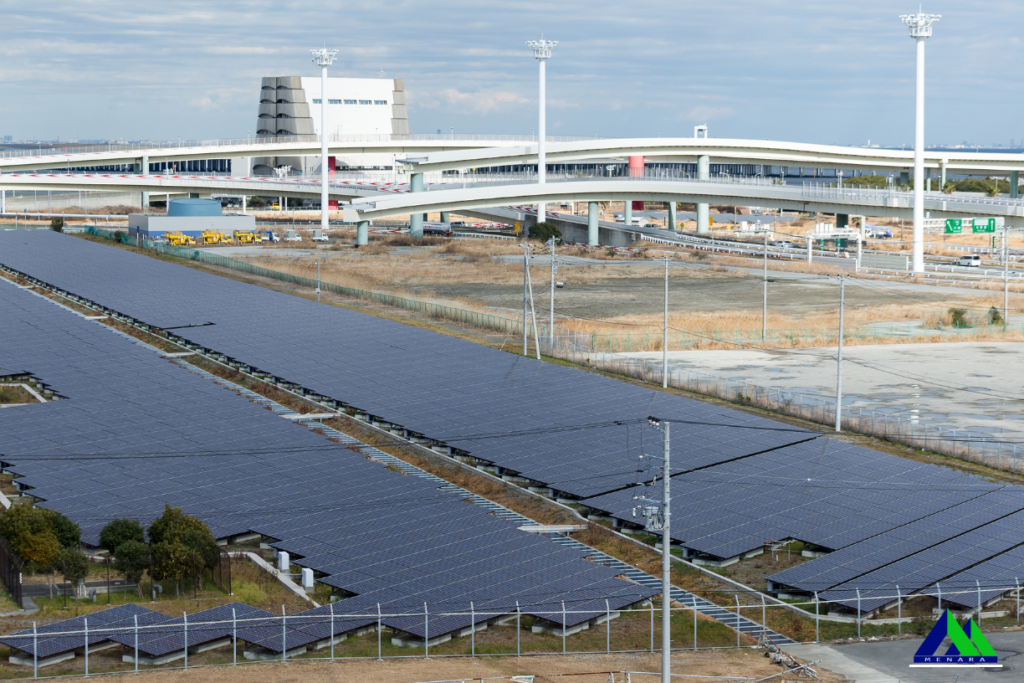

Power system stability refers to the ability of an electrical power system to regain a state of operating equilibrium after being subjected to a physical disturbance. In Brunei’s context, this encompasses:
- Voltage stability
- Frequency stability
- Rotor angle stability
These components are crucial for ensuring a reliable and efficient power supply across the country.
The Role of Power System Stability in Brunei’s Infrastructure
Brunei’s economy, largely dependent on the oil and gas sector, requires a stable and reliable power supply for its industrial operations. Moreover, as the country pursues economic diversification, sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and services also demand consistent electrical power. Stability is therefore vital for:
- Industrial Operations: Ensuring uninterrupted production in oil refineries and manufacturing plants.
- Economic Diversification: Supporting the growth of new industries and businesses.
- Public Services: Maintaining essential services such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
- Quality of Life: Providing reliable power to residential areas, enhancing the standard of living.
Challenges in Maintaining Power System Stability
Brunei faces several challenges in maintaining power system stability:
- Climate Factors: The tropical climate, with its high humidity and occasional severe weather, can stress electrical infrastructure.
- Aging Infrastructure: Some of Brunei’s power generation and transmission systems are aging, requiring upgrades and maintenance.
- Increasing Demand: Economic growth and urbanization are leading to higher power demands, putting pressure on the existing system.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: As Brunei explores renewable energy options, integrating these variable sources into the grid presents new stability challenges.
Strategies for Enhancing Power System Stability
To address these challenges, Brunei’s electrical engineers and policymakers are implementing various strategies:
- Grid Modernization: Upgrading transmission and distribution systems with smart grid technologies to improve monitoring and control.
- Enhanced Forecasting: Implementing advanced weather and demand forecasting systems to anticipate and mitigate potential stability issues.
- Robust Protection Systems: Deploying state-of-the-art protection relays and circuit breakers to quickly isolate faults and prevent widespread outages.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Exploring battery storage systems to balance load fluctuations and support renewable energy integration.
- Demand Response Programs: Implementing programs to manage peak loads and improve overall system stability.
The Role of Electrical Engineers
Electrical engineers play a crucial role in maintaining and improving power system stability in Brunei. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting stability studies and simulations
- Designing and implementing control systems
- Developing and maintaining protection schemes
- Analyzing system performance and recommending improvements
Continuous professional development and staying abreast of technological advancements are essential for these engineers to effectively manage Brunei’s evolving power system.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Looking ahead, Brunei is poised to embrace innovative technologies to further enhance power system stability:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: For predictive maintenance and real-time system optimization.
- Wide Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS): To provide a comprehensive view of the power system’s dynamic behavior.
- Microgrids: To improve local reliability and facilitate the integration of distributed energy resources.
These technologies will not only improve stability but also increase the efficiency and sustainability of Brunei’s power system.
Conclusion
Power system stability is a cornerstone of Brunei’s electrical infrastructure, underpinning its economic activities and quality of life. As the nation progresses towards a more diverse and sustainable economy, the importance of maintaining a stable and reliable power system becomes even more critical. Through ongoing investment in infrastructure, adoption of advanced technologies, and the expertise of skilled electrical engineers, Brunei is well-positioned to meet the power stability challenges of the future.
The commitment to enhancing power system stability not only ensures the reliability of Brunei’s electrical supply but also supports the nation’s broader goals of economic diversification and sustainable development. As Brunei continues to evolve, the role of power system stability in shaping its future cannot be underestimated.







Designing Energy Efficient Electrical Systems in Brunei
[…] and environmental factors. As technology in Brunei advances and energy costs continue to rise, the importance of efficient design will only […]