Table of Contents

Brunei’s power grid management has evolved significantly from its early dependence on oil and gas-driven electricity generation. The sultanate has strategically developed its electrical infrastructure to support economic diversification and meet growing energy demands. This transformation reflects Brunei’s commitment to modernizing its national energy systems while maintaining reliability and efficiency.
Current Power Generation Landscape
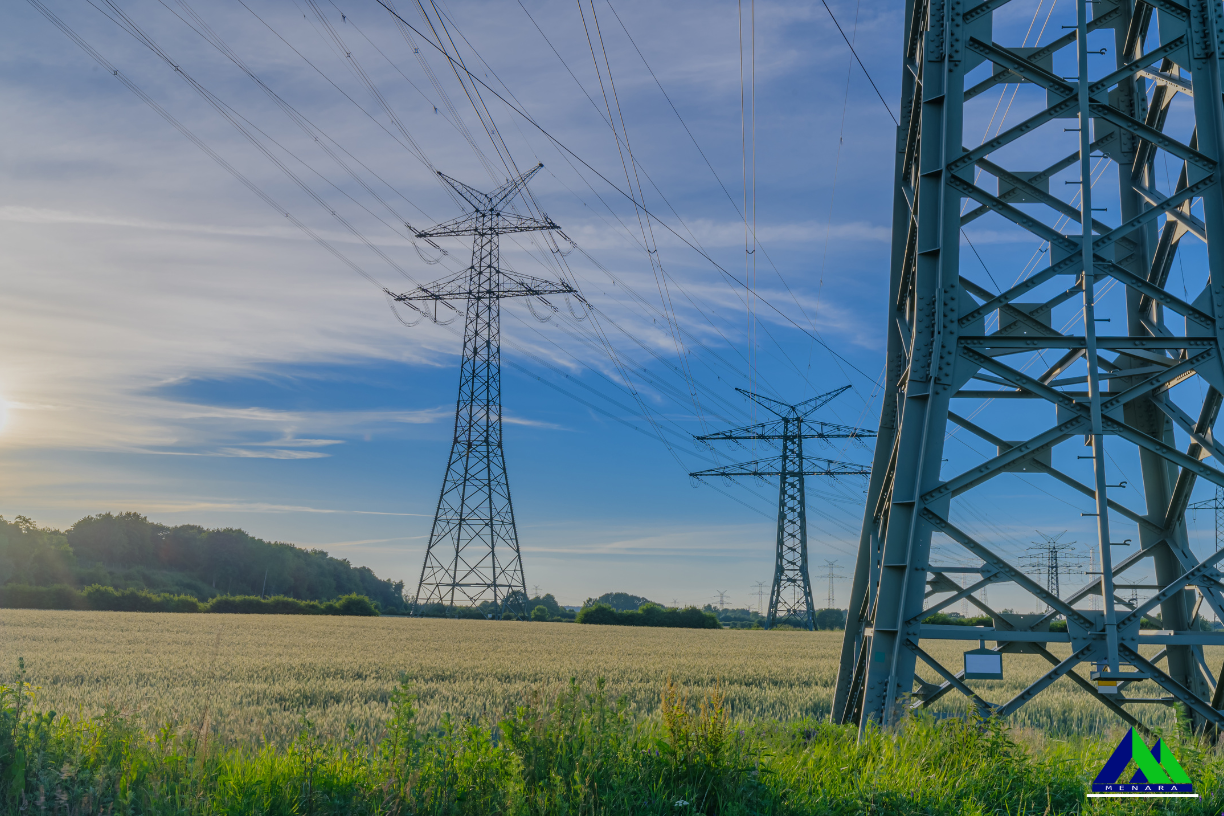
The power generation in Brunei primarily relies on natural gas-fired power plants, with increasing investments in renewable energy technologies. The nation’s electrical grid must balance traditional fossil fuel-based generation with emerging sustainable energy sources. This transition requires sophisticated grid management techniques to ensure stable and consistent power distribution across the sultanate.
Technological Challenges in Grid Management
Mechanical and electrical engineers face complex challenges in managing Brunei’s power grid. These include managing voltage fluctuations, preventing transmission losses, and integrating renewable energy sources into the existing infrastructure. The geographical diversity of Brunei’s terrain adds complexity to power transmission and distribution networks.
Smart Grid Technologies
Brunei has been progressively implementing smart grid technologies to enhance power management capabilities. These advanced systems utilize real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated control mechanisms. Mechanical engineers play a crucial role in designing and implementing these sophisticated grid management solutions that improve overall energy efficiency and reliability.
Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of renewable energy sources presents both opportunities and challenges for Brunei’s power grid. Solar and biomass energy projects are being developed to diversify the nation’s energy portfolio. Mechanical engineers are instrumental in designing grid interconnection systems that can smoothly incorporate these variable energy sources while maintaining grid stability.
Infrastructure Resilience and Maintenance
Grid infrastructure resilience is a critical concern for Brunei’s power management strategy. Engineers develop comprehensive maintenance protocols and implement advanced monitoring systems to prevent potential disruptions. This includes developing robust protection mechanisms against environmental challenges and potential technical failures.
Cybersecurity in Power Grid Management
As power systems become increasingly digital, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical consideration. Mechanical and electrical engineers collaborate to develop secure communication protocols and advanced protection mechanisms for the national power grid. These efforts ensure the integrity and reliability of Brunei’s electrical infrastructure against potential digital threats.
Critical strategies involve:
- Developing secure communication protocols
- Implementing advanced digital protection mechanisms
- Creating multi-layered security architectures
- Continuous threat assessment and mitigation
Economic and Environmental Considerations
Power grid management in Brunei must balance economic feasibility with environmental sustainability. Engineers are tasked with developing cost-effective solutions that reduce carbon emissions and support the nation’s commitment to sustainable development. This involves optimizing existing infrastructure and investing in advanced, efficient technologies.
Digital Transformation and Grid Intelligence
The digital transformation of Brunei’s power grid involves implementing advanced analytics, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. These innovations enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and more efficient energy distribution. Mechanical engineers are at the forefront of designing and implementing these intelligent grid systems.
Future Grid Modernization Strategies
Brunei’s future power grid management strategies focus on creating a more flexible, resilient, and sustainable electrical infrastructure. This includes investments in energy storage technologies, advanced grid management systems, and increased renewable energy capacity. The goal is to develop a robust and adaptable power grid that can meet the sultanate’s evolving energy requirements.
Brunei’s future power grid management strategies focus on:
- Creating flexible electrical infrastructure
- Developing energy storage technologies
- Increasing renewable energy capacity
- Enhancing grid adaptability and resilience
International Collaboration and Technology Transfer
Brunei is actively engaging in international collaborations to enhance its power grid management capabilities. These partnerships involve knowledge exchange, technology transfer, and collaborative research initiatives with global experts in power systems engineering. Such collaborations help Brunei stay at the forefront of grid management innovation.
Training and Local Capacity Development
Developing local engineering talent is crucial for sustainable power grid management. Brunei has invested in specialized training programs and educational initiatives to build a skilled workforce capable of managing complex electrical infrastructure. These efforts ensure long-term sustainability and technological advancement in the power sector.
Developing local engineering talent involves:
- Specialized training programs
- Educational initiatives in power systems engineering
- Scholarship and professional development opportunities
- Collaboration with international technical institutions
Conclusion
Power grid management in Brunei represents a complex and dynamic field that requires continuous innovation, strategic planning, and technological expertise to ensure clean energy production. As the sultanate continues to develop its electrical infrastructure, mechanical and electrical engineers will play a pivotal role in creating efficient, sustainable, and resilient power systems that support national development goals.