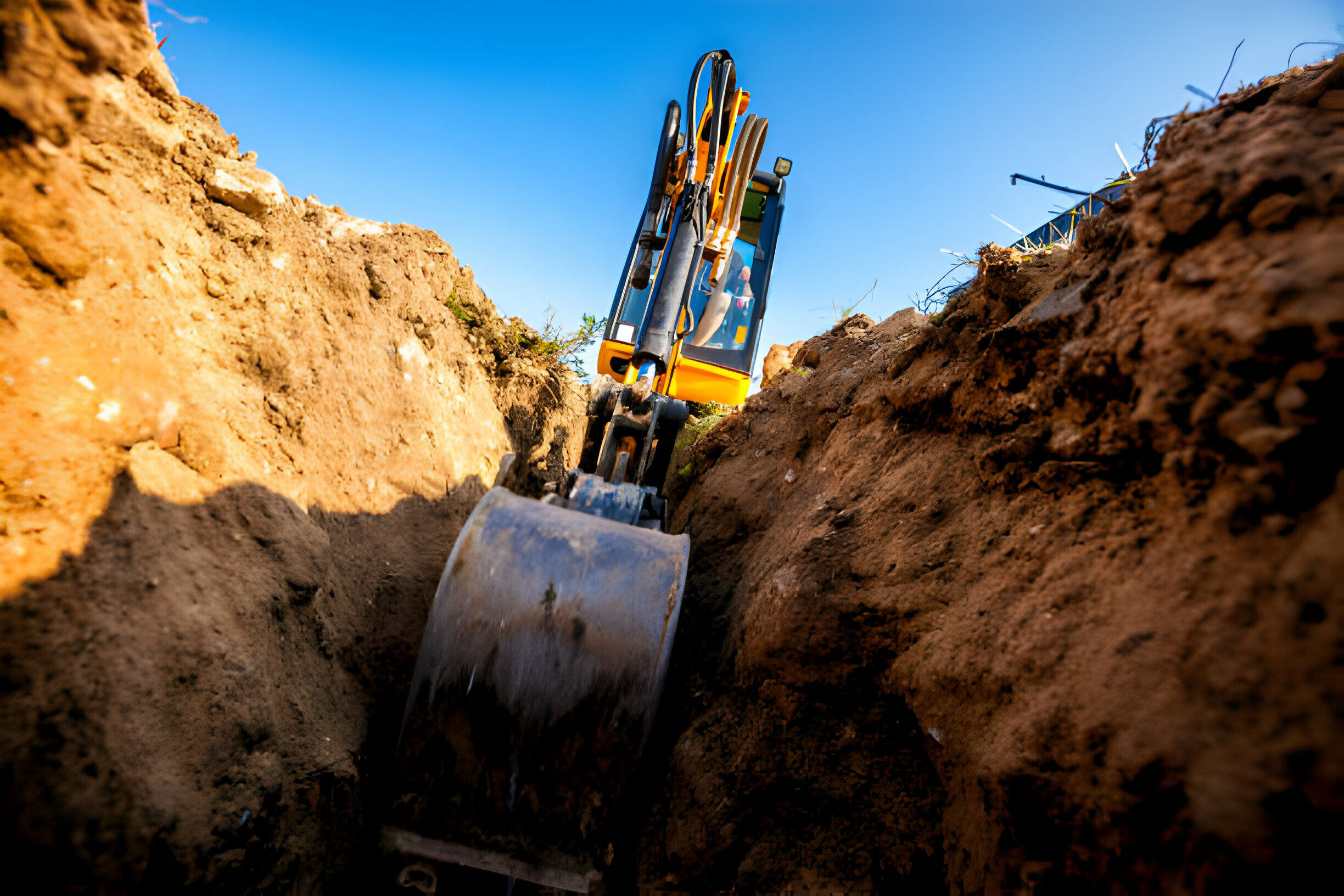
In construction, excavation work hazards and control measures are crucial for safety. Excavation involves digging and removing earth to create foundations, trenches, or other structures. Hazards include cave-ins, falling materials, and equipment accidents. These hazards can result in serious injuries or fatalities.
Control measures, such as proper training, protective systems, and regular inspections, are essential to mitigate risks. Compliance with safety regulations and protocols is imperative to ensure a safe working environment. Prioritizing safety in excavation work not only protects workers but also prevents project delays and costly accidents.
Top 5 Excavation Work Hazards and Control Measures
Cave-ins:
Excavation sites are prone to cave-ins, which occur when the walls of a trench collapse unexpectedly. These incidents can result in severe injuries or fatalities. To mitigate this risk, proper shoring, sloping, or benching techniques must be employed based on the soil type and depth of the trench. Shoring involves installing support systems such as hydraulic jacks or metal braces to prevent soil movement.
Sloping entails cutting the trench walls at an angle to stabilize them, while benching creates horizontal levels within the trench to reduce the risk of collapse. These excavation work hazards and control measures reduce the chances of injuries. Regular inspections of the trench and surrounding area should be conducted to identify any signs of instability, such as cracking or shifting soil.
Falls:
Workers in excavation sites are at risk of falls from heights, particularly when working on scaffolding, ladders, or unstable surfaces. To prevent falls, it’s essential to provide adequate fall protection equipment, such as harnesses, guardrails, and safety nets. Workers should also receive training on how to properly use this equipment and be aware of potential fall hazards on the site. All elevated work areas should be inspected regularly to ensure they meet safety standards and are free from any defects or hazards that could cause accidents.
Struck-by Accidents:
Excavation sites often involve heavy machinery and equipment, increasing the risk of workers being struck by moving vehicles or falling objects. To minimize the likelihood of struck-by accidents, strict traffic control excavation work hazards and control measures should be implemented, including designated walkways, barriers, and warning signs.
All equipment operators must undergo thorough training and adhere to established safety protocols when operating machinery. Workers should wear high-visibility clothing and hard hats to enhance their visibility and protect them from falling debris.
Hazardous Atmospheres:
Confined spaces within excavation sites can harbor hazardous atmospheres, such as toxic gases or low oxygen levels, posing serious health risks to workers. To address this hazard, proper ventilation systems should be installed to ensure adequate airflow and prevent the buildup of harmful gases. Workers should be equipped with gas detectors and respiratory protection devices to detect and mitigate potential hazards. Before entering a confined space, thorough atmospheric testing must be conducted to assess the air quality and determine if it’s safe for entry.
Utility Strikes:
Excavation work often involves digging near underground utilities, such as gas lines, electrical cables, or water pipes, increasing the risk of accidental strikes. To avoid damaging these utilities and causing potentially catastrophic incidents, it’s essential to obtain accurate utility maps and perform utility locates before excavation begins.
Workers should use non-destructive digging techniques, such as hydro excavation, to safely expose underground utilities without causing damage. Proper signage and marking should be used to indicate the presence of buried utilities and warn workers of potential hazards.
Conclusion
Excavation work hazards pose significant risks to workers if not properly managed. By implementing effective excavation work hazards and control measures, employers can mitigate these risks and ensure a safe working environment for all personnel involved. Regular training, inspections, and adherence to safety protocols are essential to prevent accidents and injuries in excavation sites.